Google Patent Parser
Using the ScrapeOps Parser API you can scrape Google Patent Pages without having to maintain your own product parsers.
Simply send the HTML of the Google Patent Pages to the Parser API endpoint, and receive the data in structured JSON format.
Google Patent Parser API Endpoint:
"https://parser.scrapeops.io/v2/google"
The Google Patent Parser supports the following page types:
Authorisation - API Key
To use the ScrapeOps Parser API, you first need an API key which you can get by signing up for a free account here.
Your API key must be included with every request using the api_key query parameter otherwise the API will return a 403 Forbidden Access status code.
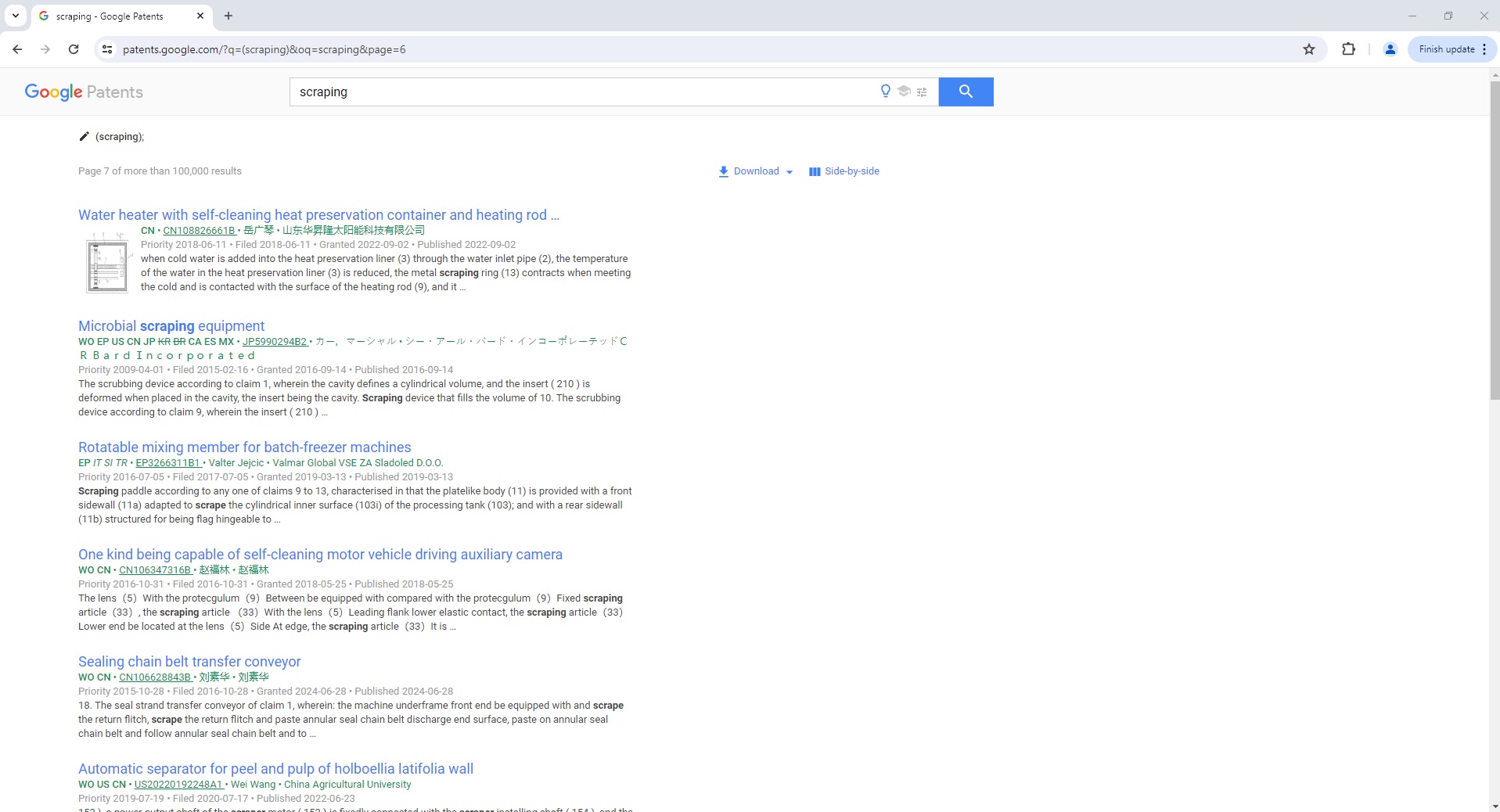
Google Patent Search Page Parser
To use the Parser API without the ScrapeOps Proxy Aggregator, you first need to retrieve the HTML of the page you want to extract the data from.
For example, here we retrieve the HTML from the following Google Patent Search Page with a very simple GET request:
import requests
response = requests.get('https://patents.google.com/?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping&page=6')
if response.status_code == 200:
html = response.text
print(html)
Next, we send this HTML to the ScrapeOps Parser API for data extraction using a POST request:
import requests
response = requests.get('https://patents.google.com/?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping&page=6')
if response.status_code == 200:
html = response.text
data = {
'url': 'https://patents.google.com/?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping&page=6',
'html': html,
}
response = requests.post(
url='https://parser.scrapeops.io/v2/google',
params={'api_key': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
json=data
)
print(response.json())
The API will return a JSON response with the following data (status, data, url):
{
"data": {
"pagination": [
{
"number": 1,
"url": "https://patents.google.com/?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping&peid=6210575c50458%3Ac4%3Ae2bb3cce"
},
{
"number": 6,
"url": "https://patents.google.com/?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping&page=5&peid=621058ca69380%3A160%3Aea08663d"
}
...
],
"related_searches": null,
"search_information": {
"count": 100000,
"count_displayed": "Page 7 of more than 100,000 results",
"deduplicate_by": "Family",
"group_by": "None",
"page_size": "10",
"query": "scraping",
"sort_by": "Relevance"
},
"search_results": [
{
"assignee": "山东华昇隆太阳能科技有限公司",
"date_info": {
"filed_date": "2018-06-11",
"granted_date": "2022-09-02",
"priority_date": "2018-06-11",
"published_date": "2022-09-02"
},
"figure": "https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/f7/29/bc/f9ba89964453aa/HDA0001691842080000011.png",
"inventor": "岳广琴",
"jurisdictions": [
"CN"
],
"pdf": "https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/d6/35/e8/06d6ee9bfa64d2/CN108826661B.pdf",
"snippet": "when cold water is added into the heat preservation liner (3) through the water inlet pipe (2), the temperature of the water in the heat preservation liner (3) is reduced, the metal scraping ring (13) contracts when meeting the cold and is contacted with the surface of the heating rod (9), and it …",
"title": "Water heater with self-cleaning heat preservation container and heating rod …",
"url": "https://patents.google.com/patent/CN113713442A/en?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping&peid=621055b4be6f0%3Aa%3Ae539b329"
},
{
"assignee": "シー・アール・バード・インコーポレーテッドC R Bard Incorporated",
"date_info": {
"filed_date": "2015-02-16",
"granted_date": "2016-09-14",
"priority_date": "2009-04-01",
"published_date": "2016-09-14"
},
"figure": "https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/d3/b2/1a/aa3489e2cb4904/0005990294-2.png",
"inventor": "カー,マーシャル",
"jurisdictions": [
"MX",
"ES",
"CA",
"BR",
"KR",
"JP",
"CN",
"US",
"EP",
"WO"
],
"pdf": "https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/65/30/c6/7968fa25e25e9c/JP5990294B2.pdf",
"snippet": "The scrubbing device according to claim 1, wherein the cavity defines a cylindrical volume, and the insert ( 210 ) is deformed when placed in the cavity, the insert being the cavity. Scraping device that fills the volume of 10. The scrubbing device according to claim 9, wherein the insert ( 210 ) …",
"title": "Microbial scraping equipment",
"url": "https://patents.google.com/patent/CN103501946B/en?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping&peid=621055ca7aa48%3Ab%3Ad2eb26b6"
}
...
],
"summary": {
"top_assignees": [
{
"name": "Ricoh Company, Ltd.",
"value": "0.9%"
},
{
"name": "株式会社リコー",
"value": "0.9%"
}
...
]
}
},
"status": "parse_successful",
"url": "https://patents.google.com/patent/CN113713442A/en?q=(scraping)&oq=scraping"
}
A full example JSON response can be found here.
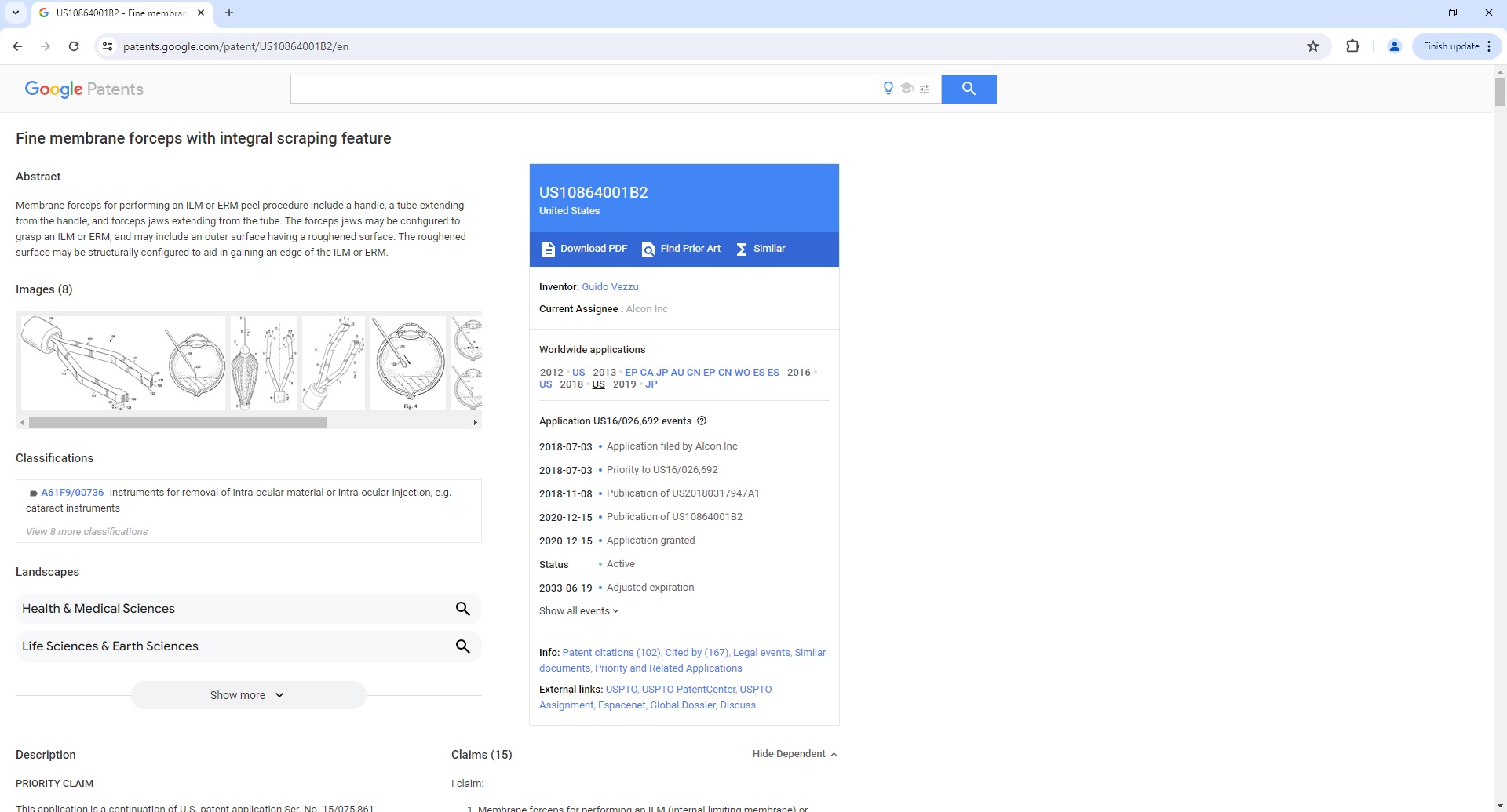
Google Patent Article Page Parser
To use the Parser API without the ScrapeOps Proxy Aggregator, you first need to retrieve the HTML of the page you want to extract the data from.
For example, here we retrieve the HTML from the following Google Patent Article Page with a very simple GET request:
import requests
response = requests.get('https://patents.google.com/patent/US10864001B2/en')
if response.status_code == 200:
html = response.text
print(html)
Next, we send this HTML to the ScrapeOps Parser API for data extraction using a POST request:
import requests
response = requests.get('https://patents.google.com/patent/US10864001B2/en')
if response.status_code == 200:
html = response.text
data = {
'url': 'https://patents.google.com/patent/US10864001B2/en',
'html': html,
}
response = requests.post(
url='https://parser.scrapeops.io/v2/google',
params={'api_key': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
json=data
)
print(response.json())
The API will return a JSON response with the following data (status, data, url):
{
"data": {
"applications": {
"claiming_priority_applications": [
{
"application": "US13/713,782",
"filing_date": "2012-12-13",
"title": "Fine membrane forceps with integral scraping feature"
},
{
"application": "US15/075,861",
"filing_date": "2016-03-21",
"title": "Fine membrane forceps with integral scraping feature"
}
...
],
"parent_applications": [
{
"application": "US15/075,861",
"filing_date": "2016-03-21",
"priority_date": "2012-12-13",
"relation": "Continuation",
"title": "Fine membrane forceps with integral scraping feature"
}
],
"priority_applications": [
{
"application": "US16/026,692",
"filing_date": "2018-07-03",
"priority_date": "2012-12-13",
"title": "Fine membrane forceps with integral scraping feature"
}
]
},
"cited_by": [
{
"assignee": "Alcon Inc.",
"priority_date": "2019-08-29",
"publication_date": "2021-10-26",
"publication_number": "USD934424S1 *",
"title": "360 degree actuation handle"
},
{
"assignee": "Alcon Inc.",
"priority_date": "2019-08-29",
"publication_date": "2022-11-08",
"publication_number": "US11490915B2",
"title": "Actuation mechanism with grooved actuation levers"
}
...
],
"concepts": [
{
"count": "70",
"name": "membrane",
"query_match": "0.000",
"sections": "title,claims,abstract,description"
},
{
"count": "17",
"name": "scraping",
"query_match": "0.000",
"sections": "title,description"
}
...
],
"information": {
"abstract": "Membrane forceps for performing an ILM or ERM peel procedure include a handle, a tube extending from the handle, and forceps jaws extending from the tube. The forceps jaws may be configured to grasp an ILM or ERM, and may include an outer surface having a roughened surface. The roughened surface may be structurally configured to aid in gaining an edge of the ILM or ERM.",
"claims": "I claim: 1. Membrane forceps for performing an ILM (internal limiting membrane) or ERM (epiretinal membrane) peel procedure, comprising: a handle; a tube extending from the handle; and forceps jaws extending from the tube, the forceps jaws being configured to grasp an ILM or ERM between two opposing grip faces configured to abut each other when the forceps jaws are closed, the forceps jaws also comprising an outer surface, external to the grip faces, having a laser cut array of peaks, ...",
"classifications": [
{
"code": "A61F9/00736",
"description": "Instruments for removal of intra-ocular material or intra-ocular injection, e.g. cataract instruments"
},
{
"code": "A61B17/29",
"description": "Forceps for use in minimally invasive surgery"
}
...
],
"description": "PRIORITY CLAIM This application is a continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 15/075,861 titled “FINE MEMBRANE FORCEPS WITH INTEGRAL SCRAPING FEATURE”, filed on Mar. 21, 2016, whose inventor is Guido Vezzu which is a continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 13/713,782 titled “FINE MEMBRANE FORCEPS WITH INTEGRAL SCRAPING FEATURE”, filed on Dec. 13, 2012, whose inventor is Guido Vezzu, both of which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety as though fully and completely set forth herein. BACKGROUND The devices, systems, and methods disclosed herein relate generally to surgical instruments and techniques, and more particularly, to surgical instruments and techniques for treating an ocular condition. Internal limiting membrane (ILM) removal and epi-retinal membrane (ERM) removal are useful surgical treatments of different macular surface diseases. However, the surgical techniques for ILM and ERM peeling require skill and patience. ...",
"images": [
"https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/91/0e/d7/2c2c3bc072972f/US10864001-20201215-D00000.png",
"https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/be/93/f4/f0f48e0405dc94/US10864001-20201215-D00001.png",
"https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/52/48/e4/3666b2c77d82de/US10864001-20201215-D00002.png"
...
],
"landscapes": [
{
"link": "https://patents.google.com#",
"query": "Health & Medical Sciences"
},
{
"link": "https://patents.google.com#",
"query": "Life Sciences & Earth Sciences"
}
]
},
"knowledge": {
"application_events": [
{
"date": "2018-07-03",
"title": "Application filed by Alcon Inc"
},
{
"date": "2018-07-03",
"title": "Priority to US16/026,692"
}
...
],
"country": "United States",
"current_assignee": [
"Alcon Inc"
],
"inventor": [
"Guido Vezzu"
],
"publication_number": "US10864001B2",
"worldwide_applications": [
{
"cc": "US",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"cc": "EP",
"year": "2013"
}
...
]
},
"legal_events": [
{
"code": "FEPP",
"date": "2018-07-03",
"description": "Free format text: ENTITY STATUS SET TO UNDISCOUNTED (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: BIG.); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY",
"title": "Fee payment procedure"
},
{
"code": "AS",
"date": "2018-07-26",
"description": "Owner name: ALCON RESEARCH, LTD., TEXAS Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:VEZZU, GUIDO;REEL/FRAME:046470/0041 Effective date: 20121217",
"title": "Assignment"
}
...
],
"patent_citiations": [
{
"assignee": "А.И. Горбань",
"priority_date": "1958-02-17",
"publication_date": "1958-11-30",
"publication_number": "SU117617A1",
"title": "Collet Tweezers"
},
{
"assignee": "Maikurosaajikaru Adominisutora",
"priority_date": "1980-11-07",
"publication_date": "1982-07-09",
"publication_number": "JPS57110238A",
"title": "Grip apparatus"
}
...
],
"similar_documents": [
{
"publication": "US10864001B2",
"publication_date": "2020-12-15",
"title": "Fine membrane forceps with integral scraping feature"
},
{
"publication": "CN106163464B",
"publication_date": "2020-10-27",
"title": "Surgical instrument with adhesion-optimized edge conditions"
}
...
],
"title": "Fine membrane forceps with integral scraping feature"
},
"status": "parse_successful",
"url": "https://patents.google.com/patent/US10864001B2/en"
}
A full example JSON response can be found here.
Proxy API Integration
The ScrapeOps Parser API is integrated into the ScrapeOps Proxy API Aggregator and can be used for free by using the Auto Extract functionality.
So if you already have a Proxy API Aggregator plan then use the Parser API for no extra charge.
The following example shows you how to use the Parser API via a Python Requests based scraper using the Proxy API Aggregator:
import requests
response = requests.get(
url='https://proxy.scrapeops.io/v1/',
params={
'api_key': 'YOUR_API_KEY',
'url': 'https://patents.google.com/patent/US10864001B2/en',
'auto_extract': 'google'
}
)
print(response.json())